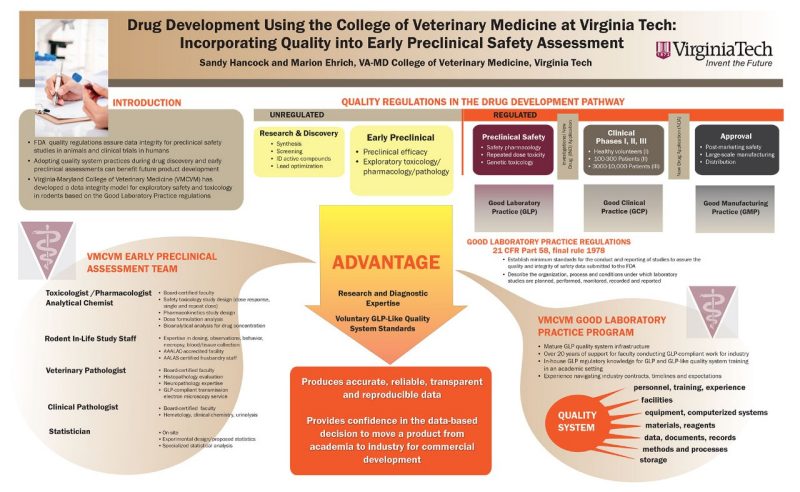
Analytical Chemistry Research Laboratory (pharmacology and toxicology)
The Analytical Chemistry Research Laboratory (Pharmacology/Toxicology) at the Virginia-Maryland College of Veterinary Medicine (VMCVM) provides a variety of assays for qualitative and quantitative determination drugs, heavy metals, and toxicants (including pesticides), as well as capability for pharmacokinetic and toxicokinetic studies.
Analytical instrumentation
An overview of the laboratory and its instrumentation
Research capabilities
1) Definitions
“Pharmacokinetics is the study of drug disposition in the body and focuses on the changes in drug plasma concentration. For any given drug and dose, the plasma concentration of the drug will rise and fall according to the rates of three processes: absorption, distribution, and elimination. Absorption of a drug refers to the movement of drug into the bloodstream, with the rate dependent on the physical characteristics of the drug and its formulation. Distribution of a drug refers to the process of a drug leaving the bloodstream and going into the organs and tissues. Elimination of a drug from the blood relies on two processes: biotransformation (metabolism) of a drug to one or more metabolites, primarily in the liver; and the excretion of the parent drug or its metabolites, primarily by the kidneys.”
— Brenner & Stevens, Pharmacology
Toxicokinetics (TK) is similar, with TK being the study of absorption, distribution, and elimination of poisons, including the elimination rate and half-life (t1/2).
2) Procedures
Quantification of exogenous substances (drugs/ toxicants) and kinetic analyses
Pharmacokinetics (PK) can be used for drug monitoring, including determination of safe dosing levels, appropriate frequency of dosing, and duration of effective drug plasma levels. Expertise in pharmacokinetic modeling is available. The laboratory is also associated with FARAD (Food Animal Residue Avoidance Database), which assists veterinarians and others with appropriate extra label drug use in food-producing animals.
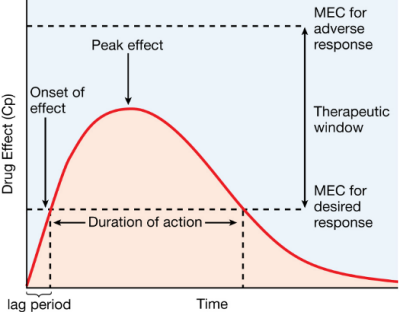
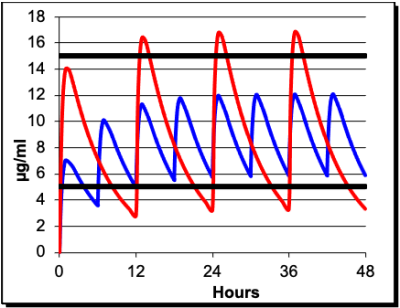
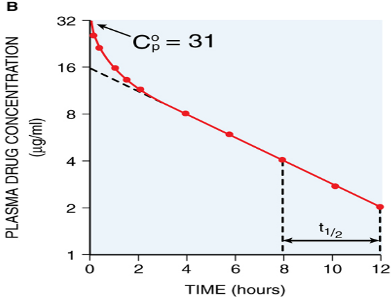
Diagrams from Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics and KinetiClass, J Wilcke
The Analytical Research laboratory has assays currently available for quantitation of aflatoxins, anticoagulant rodenticides, barbiturates, carbamate insecticides, nitrates, Vitamin A, Vitamin E, and vomitoxin. Screening for metals/minerals and pesticides can also be done.
a. Heavy Metal analysis using ICP/MS
Among the metals and minerals that can be screened and quantitated by ICP-MS are arsenic, cadmium, calcium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium molybdenum, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, sodium, and zinc.
b. Drug Discovery Support
Preclinical drug discovery involves collection of a variety of endpoints for which VMCVM is uniquely qualified to provide, with able assistance from board-certified professionals in pharmacology, toxicology, anatomic pathology, and clinical pathology.
In addition, VMCVM has support services in laboratory animal husbandry (TRACSS), analytical chemistry, statistics, and good laboratory practices/quality control. Services not specifically listed under the Analytical Research Laboratory (pharmacology and toxicology) are available and can be accessed via Investigator Resources. These services include animal care and support (TRACSS), pathology (ViTALS), statistics, and Good Laboratory Practices/Quality Assurance.
Toxicology sample submission
Samples may be submitted to the Analytical Research Laboratory (Pharmacology/Toxicology) at Virginia-Maryland College of Veterinary Medicine or to outside laboratories (e.g., Michigan State University, Iowa State University, University of Pennsylvania New Bolton Center, Purdue College of Veterinary Medicine, Kansas State University, University of Missouri.
Submissions for toxicology can involve consultation with a toxicologist before analyses are done and interpretation of results afterwards. Written results are provided.
Samples for analysis at VMCVM should be submitted by Wednesday to be run on Thursday with results by Friday. Costs for samples are determined by Analytical Instrumentation used. Due to limited staffing, sample processing may not be available every week. Prior to sample submission, please contact the lab manager at mmassy24@vt.edu to confirm availability of testing for that week.
Bolded names indicate Analytical Research Laboratory personnel and other faculty in the VMCVM Department of Biomedical Sciences and Pathobiology.
Pharmacokinetics and pulmonary distribution of Draxxin® (tulathromycin) in healthy adult horses. Leventhal HR, McKenzie HC, Estell K, Council-Troche M, Davis JL. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Mar 14. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12968. Online ahead of print. PMID: 33719056
Study design synopsis: Designing and performing pharmacokinetic studies for systemically administered drugs in horses. Bermingham E, Davis JL, Whittem T. Equine Vet J. 2020 Sep;52(5):643-650. doi: 10.1111/evj.13312.PMID: 32748990
Pharmacokinetics and safety of repeated oral dosing of acetaminophen in adult horses. Mercer MA, McKenzie HC, Davis JL, Wilson KE, Hodgson DR, Cecere TE, McIntosh BJ. Equine Vet J. 2020 Jan;52(1):120-125. doi: 10.1111/evj.13112. Epub 2019 Apr 16.PMID: 30900298
Pharmacodynamic effects of pioglitazone on high molecular weight adiponectin concentrations and insulin response after oral sugar in equids. Legere RM, Taylor DR, Davis JL, Bello K, Parker C, Judd RL, Wooldridge AA. J Equine Vet Sci. 2019 Nov;82:102797. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2019.102797. Epub 2019 Sep 24.PMID: 31732109
Integration of Food Animal Residue Avoidance Databank (FARAD) empirical methods for drug withdrawal interval determination with a mechanistic population-based interactive physiologically based pharmacokinetic (iPBPK) modeling platform: example for flunixin meglumine administration. Li M, Cheng YH, Chittenden JT, Baynes RE, Tell LA, Davis JL, Vickroy TW, Riviere JE, Lin Z. Arch Toxicol. 2019 Jul;93(7):1865-1880. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02464-z. Epub 2019 Apr 25.PMID: 31025081
Pharmacokinetics of intrarectal altrenogest in horses. Ellis KE, Council-Troche RM, Von Dollen KA, Beachler TM, Bailey CS, Davis JL, Lyle SK.J Equine Vet Sci. 2019 Jan;72:41-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jevs.2018.10.001. Epub 2018 Oct 10.PMID: 30929782
Photo-triggered release of 5-fluorouracil from a MOF drug delivery vehicle. Roth Stefaniak K , Epley CC , Novak JJ , McAndrew ML , Cornell HD , Zhu J , McDaniel DK, Davis JL , Allen IC , Morris AJ , Grove TZ. Chem Commun (Camb). 2018 Jul 5;54(55):7617-7620. doi: 10.1039/c8cc01601a.PMID: 29926872
Targeted delivery of persulfides to the gut: Effects on the microbiome. Dillon KM, Morrison HA, Powell CR, Carrazzone RJ, Ringel-Scaia VM, Winckler EW, Council-Troche RM, Allen IC, Matson JB. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Mar 8;60(11):6061-6067. doi: 10.1002/anie.202014052. Epub 2021 Jan 29.PMID: 33511734
Studies exploring the interaction of the organophosphorus compound paraoxon with fullerenes. Magnin G, Bissel P, Council-Troche RM, Zhou Z, Ehrich M. ACS Omega. 2019 Oct 28;4(20):18663-18667. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b02587. eCollection 2019 Nov 12.PMID: 31737826
Pulmonary exposure to Magnéli Phase Titanium Suboxides results in significant macrophage abnormalities and decreased lung function. McDaniel DK, Ringel-Scaia VM, Morrison HA, Coutermarsh-Ott S, Council-Troche M, Angle JW, Perry JB, Davis G, Leng W, Minarchick V, Yang Y, Chen B, Reece SW, Brown DA, Cecere TE, Brown JM, Gowdy KM, Hochella MF Jr, Allen IC. Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 28;10:2714. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02714. eCollection 2019.PMID: 31849940
Cardiovascular and respiratory effects of two doses of fentanyl in the presence or absence of bradycardia in isoflurane-anesthetized dogs. Williamson AJ, Soares JH, Henao-Guerrero N, Council-Troche RM, Pavlisko ND. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2018 Jul;45(4):423-431. doi: 10.1016/j.vaa.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 19.PMID: 29716836 Clinical Trial.
Nonclinical toxicology and toxicokinetic profile of an oral Lanthionine Synthetase C-Like 2 (LANCL2) agonist, BT-11. Leber A, Hontecillas R, Zoccoli-Rodriguez V, Ehrich M, Davis J, Chauhan J, Bassaganya-Riera J. Int J Toxicol. 2019 Mar/Apr;38(2):96-109. doi: 10.1177/1091581819827509. Epub 2019 Feb 21.PMID: 30791754
Synthesis and evaluation of doxorubicin-loaded gold nanoparticles for tumor-targeted drug delivery. Du Y, Xia L, Jo A, Davis RM, Bissel P, Ehrich MF, Kingston DGI. Bioconjug Chem. 2018. Feb 21;29(2):420-430. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00756. Epub 2018 Jan 11.PMID: 29261297
Cerium oxide nanoparticles in neuroprotection and considerations for efficacy and safety. Rzigalinski BA, Carfagna CS, Ehrich M. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2017 Jul;9(4):10.1002/wnan.1444. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1444. Epub 2016 Nov 8.PMID: 27860449
Trace minerals in tilapia fillets: Status in the United States marketplace and selenium supplementation strategy for improving consumer's health. Farzad R, Kuhn DD, Smith SA, O'Keefe SF, Ralston NVC, Neilson AP, Gatlin DM. PLoS One. 2019 Jun 6;14(6):e0217043. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217043. eCollection 2019.PMID: 31170189
Commercial rodent diets differentially regulate autoimmune glomerulonephritis, epigenetics and microbiota in MRL/lpr mice. Edwards MR, Dai R, Heid B, Cecere TE, Khan D, Mu Q, Cowan C, Luo XM, Ahmed SA. Int Immunol. 2017 Jun 1;29(6):263-276. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxx033.PMID: 28637300
Chronic methyl mercury toxicity in a 72 year-old athletic male from southwestern Virginia. Palmieri JR, Council-Troche M, Fralin J, McCabe A, Rzigalinski BA J. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 10:454. doi: 10.35248/2161-0495.20.10.454
Implications and significance of mercury in rice. Palmieri JR, Guthrie T, Kaur G, Collins E, Benjamin B, Brunette J, Council-Troche M, Wilson ML, Meacham S, Rzigalinski B. J Food Nutrition Metab. 2020, 3(2) 2-5. doi: 10.31487/j/JFNM.2020.02.02
A study of rare earth ion-adsorption clays: The speciation of rare earth elements on kaolinite at basic pH. Feng X, Onel O, Council-Troche M, Noble A, Yoon RH, Morris JR. Applied Clay Science 2021, 201, 205920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2020.105920
Physiological parameter values for physiologically based pharmacokinetic models in food-producing animals. Part III: Sheep and goat.
Li M, Wang YS, Elwell-Cuddy T, Baynes RE, Tell LA, Davis JL, Maunsell FP, Riviere JE, Lin Z. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Dec 22. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12938. Online ahead of print.PMID: 33350478 Review.
Physiological parameter values for physiologically based pharmacokinetic models in food-producing animals. Part II: Chicken and turkey.
Wang YS, Li M, Tell LA, Baynes RE, Davis JL, Vickroy TW, Riviere JE, Lin Z. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Dec 2. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12931. Online ahead of print.PMID: 33289178 Review.
Physiological parameter values for physiologically based pharmacokinetic models in food-producing animals. Part I: Cattle and swine.
Lin Z, Li M, Wang YS, Tell LA, Baynes RE, Davis JL, Vickroy TW, Riviere JE. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Sep;43(5):385-420. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12861. Epub 2020 Apr 8.PMID: 32270548 Review.
Impact of bovine respiratory disease on the pharmacokinetics of danofloxacin and tulathromycin in different ages of calves.
Mzyk DA, Bublitz CM, Martinez MN, Davis JL, Baynes RE, Smith GW. PLoS One. 2019 Jun 24;14(6):e0218864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218864. eCollection 2019.PMID: 31233558
Pharmacokinetics and physiologic/behavioral effects of buprenorphine administered sublingually and intravenously to neonatal foals.
Grubb TL, Kurkowski D, Sellon DC, Seino KK, Coffey T, Davis JL. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Jan;42(1):26-36. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12715. Epub 2018 Sep 21.PMID: 30242851
Pharmacokinetics of Ceftiofur Crystalline-Free Acid in Clinically Healthy Dogs (Canis lupus familiaris).
Hooper SE, Korte SW, Giguère S, Fales WH, Davis JL, Dixon LW.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2016 Mar;55(2):224-9.PMID: 27025816
Intravenous and sublingual buprenorphine in horses: pharmacokinetics and influence of sampling site. Messenger KM, Davis JL, LaFevers DH, Barlow BM, Posner LP. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2011 Jul;38(4):374-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-2995.2011.00613.x. Epub 2011 Apr 19.PMID: 21501371 Clinical Trial.
Exploratory studies with NX-13: oral toxicity and pharmacokinetics in rodents of an orally active, gut-restricted first-in-class therapeutic for IBD that targets NLRX1.
Leber A, Hontecillas R, Zoccoli-Rodriguez V, Ehrich M, Chauhan J, Bassaganya-Riera J.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2019 Oct 25:1-6. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2019.1679828. Online ahead of print.PMID: 31650868
Iridium piano stool complexes with activity against S. aureus and MRSA: it is past time to truly think outside of the box.
DuChane CM, Karpin GW, Ehrich M, Falkinham JO 3rd, Merola JS. Medchemcomm. 2019 May 14;10(8):1391-1398. doi: 10.1039/c9md00140a. eCollection 2019 Aug 1.PMID: 31534656
The safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics profile of BT-11, an oral, gut-restricted Lanthionine Synthetase C-Like 2 agonist investigational new drug for inflammatory bowel disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase I clinical trial.
Leber A, Hontecillas R, Zoccoli-Rodriguez V, Colombel JF, Chauhan J, Ehrich M, Farinola N, Bassaganya-Riera J. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2020 Mar 4;26(4):643-652. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izz094.PMID: 31077582 Clinical Trial.
Cefazolin concentration in surgically created wounds treated with negative pressure wound therapy compared to surgically created wounds treated with nonadherent wound dressings.
Coutin JV, Lanz OI, Magnin-Bissel GC, Ehrich MF, Miller EI, Werre SR, Riegel TO. Vet Surg. 2015 Jan;44(1):9-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-950X.2014.12218.x. Epub 2014 Jun 24.PMID: 24962470 Clinical Trial.
Contacts
Dr. Jennifer Davis
Supervisor, Analytical Laboratory
Phone: 540-231-2192
Email: jdavis4@vt.edu
Dr. Massy Moradihaghighi
Analytical Chemist
Phone: 540-231-4835
Email: mmassy24@vt.edu